Client-Server Integration Guide for JavaScript
This guide is for publishers with web assets who want to generate identity tokens using EUID for the RTB bidstream, generating EUID tokens on the server side and passing them to the publishers' web pages, and refreshing the tokens on the client side using the SDK for JavaScript.
This is called client-server integration because the JavaScript integration steps are client-side and some other steps are server-side.
If you prefer to integrate with EUID via only client-side JavaScript changes, see Client-Side Integration Guide for JavaScript.
For technical details about the SDK, see SDK for JavaScript Reference Guide.
Introduction
This guide outlines the basic steps that you need to consider if you are building an integration without using an SDK. For example, you need to decide how to implement user authentication and data capture, how to manage EUID identity information and use it for targeted advertising, and how to refresh tokens, deal with missing identities, and handle user opt-outs.
For a workflow diagram, see Integration Steps. See also FAQs.
For details about the EUID opt-out workflow and how users can opt out, see User Opt-Out.
To facilitate the process of establishing client identity using EUID and retrieving advertising tokens, the web integration steps provided in this guide rely on the SDK for JavaScript. For an example, see Sample Implementation.
The first-party cookie and local storage implementation details might change in the future. To avoid potential issues, be sure to rely on the functionality documented in the SDK for JavaScript API Reference for your identity management.
For integration scenarios for publishers that do not use the SDK for JavaScript, see Publisher Integration Guide, Server-Side.
If you are using Google Ad Manager and want to use the secure signals feature, first follow the steps in this guide and then follow the additional steps in the Google Ad Manager Secure Signals Integration Guide.
Integrating with Single Sign-On (SSO)
If you integrate with one or more SSO providers to offer SSO login, you might be able to retrieve the logged-in user's email address from the SSO provider to generate EUID tokens.
For details, see Publisher Integration with SSO Providers.
Integration Steps
The following diagram outlines the steps required for establishing a user's EUID token with a publisher and how the EUID token integrates with the RTB bidstream.
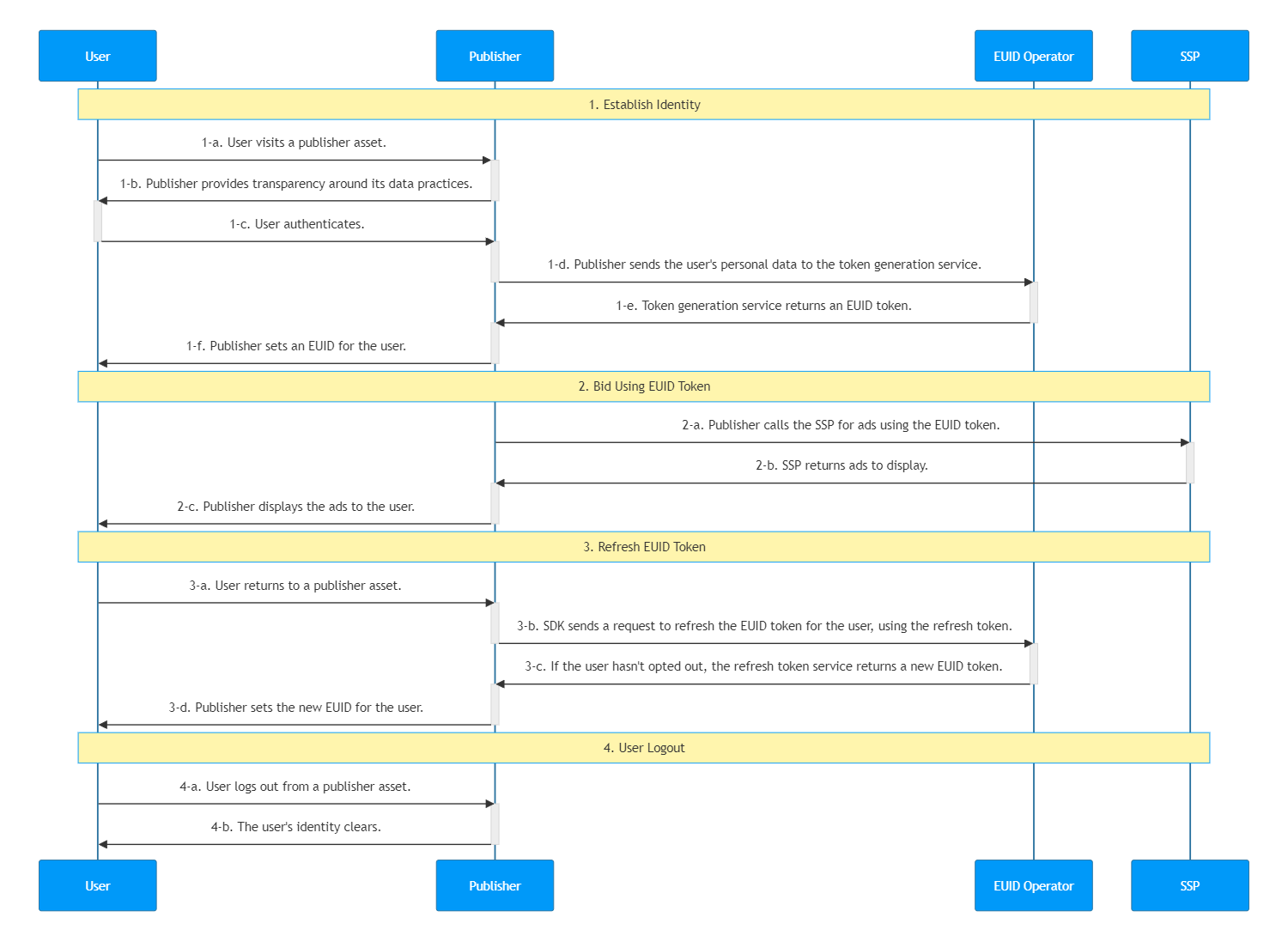
The following sections provide additional details for each step in the diagram:
- Establish identity: capture user data
- Bid Using EUID Tokens
- Refresh Tokens
- Clear Identity: User Logout
Establish Identity: Capture User Data
After authentication in step 1-c, which allows the publisher to validate the user's email address or phone number, an EUID token must be generated on the server side. The following table details the token generation steps.
| Step | Endpoint/SDK | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1-d | POST /token/generate | Use the POST /token/generate endpoint to generate an EUID token using the email address or phone number provided by the user. Make sure it is normalized. |
| 1-e | POST /token/generate | The endpoint returns an EUID token generated from the user's email address, phone number, or the respective hash. |
| 1-f | SDK for JavaScript | The SDK sends the returned EUID token from step 1-e to the SDK in the identity property of its init() function. |
| 1-g | SDK for JavaScript | Provide the SDK a callback function that will receive identity updates from the SDK and use them to initiate targeted advertising. |
Generating an EUID Token on the Server
The first step is to generate the EUID token on your server.
For details, including instructions and examples, see Server-Side Token Generation.
You will need to pass the Identity response to the SDK. See Sending the EUID Token to the SDK.
For security reasons, the API key and secret used in token generation must be called server-side. Do not store these values on the client side. For details, see Security of API Key and Client Secret.
Sending the EUID Token to the SDK
The following code examples illustrate steps 1-f and 1-g, in JavaScript and TypeScript.
- JavaScript
- TypeScript
window.__euid = window.__euid || {};
window.__euid.callbacks = window.__euid.callbacks || [];
// Step 1-f
window.__euid.callbacks.push((eventType, payload) => {
if (eventType === 'SdkLoaded') {
__euid.init({
identity : {
"advertising_token": "E4AAAAW2T2Fj-aRzN_G_t-1UP9Ndl-e1kJLCL0b9wTq0UORlRIFjIS4Mz7I3TYy6YrYyIGDwjHWZOifsnYTZawQcCwAkfyp0RbkLhB4Hznodt3ZLHrOYqFmvSrsbEuMrowfoGSJyFz3hj-Q4CArezZzamp1-aoOjJz3s-ydQADH7OapPv5iQBYBiWza3r3tBVY7drUMV8_08aBMqHuLyKzNUvws",
"identity_expires": 1724995694316,
"refresh_expires": 1727586794316,
"refresh_from": 1724995094316,
"refresh_response_key": "8yaj8hL5gS0fiB7CxvCxG25mDO3QWiqr73oF696QtiU=",
"refresh_token": "EAAABbf4KYu1LMa4+9wE7SqDIhSnSOMSmneocSaAxYl9ptV7iEOT0899ZUdtaTkSb5fHuArOtanqenPIDESXqg5uhqCDlHZfIqqq6HNBiV4ZZjPm3nA2LJAQ9Za0WydmWcpTdPSapcMyQPvW9CQTZcHNoYTVjtol4nraKDcn6ZGxea/4TA+zeFf9ohBZ8Eyt1zN+JKhB4ccvbCUeFaRrOKYyBUppGdaRiN6bL+d/uKY6XPVCw4lW7BJ87xDRb/JDfkG1bly0sIl3MWaFQK8AzEJJj8dzBYvpYAVXbvpxi/9gDEAzsdF3lT8Mdso8xj4Kx7jp79QDrIBL40E4pSDaNeNMnU8+Yo1nrQVCO2JBEy3kpvn8pUnDjxZlBTZ9I4PkmH/Q"
}
});
}
});
// Step 1-g
window.__euid.callbacks.push((eventType, payload) => {
if (eventType !== 'SdkLoaded') {
if (payload.identity) {
const advertisingToken = payload.identity.advertising_token;
// Pass advertising_token to your advertising system to use
} else {
// No identity is available. Trigger a workflow for obtaining email address if you want to use EUID for targeted advertising.
}
}
});
import { EventType, CallbackPayload } from "./CallbackManager";
window.__euid = window.__euid || {};
window.__euid.callbacks = window.__euid.callbacks || [];
// Step 1-f
window.__euid.callbacks.push((eventType: EventType, payload: CallbackPayload) => {
if (eventType === 'SdkLoaded') {
__euid.init({
identity : {
"advertising_token": "E4AAAAW2T2Fj-aRzN_G_t-1UP9Ndl-e1kJLCL0b9wTq0UORlRIFjIS4Mz7I3TYy6YrYyIGDwjHWZOifsnYTZawQcCwAkfyp0RbkLhB4Hznodt3ZLHrOYqFmvSrsbEuMrowfoGSJyFz3hj-Q4CArezZzamp1-aoOjJz3s-ydQADH7OapPv5iQBYBiWza3r3tBVY7drUMV8_08aBMqHuLyKzNUvws",
"identity_expires": 1724995694316,
"refresh_expires": 1727586794316,
"refresh_from": 1724995094316,
"refresh_response_key": "8yaj8hL5gS0fiB7CxvCxG25mDO3QWiqr73oF696QtiU=",
"refresh_token": "EAAABbf4KYu1LMa4+9wE7SqDIhSnSOMSmneocSaAxYl9ptV7iEOT0899ZUdtaTkSb5fHuArOtanqenPIDESXqg5uhqCDlHZfIqqq6HNBiV4ZZjPm3nA2LJAQ9Za0WydmWcpTdPSapcMyQPvW9CQTZcHNoYTVjtol4nraKDcn6ZGxea/4TA+zeFf9ohBZ8Eyt1zN+JKhB4ccvbCUeFaRrOKYyBUppGdaRiN6bL+d/uKY6XPVCw4lW7BJ87xDRb/JDfkG1bly0sIl3MWaFQK8AzEJJj8dzBYvpYAVXbvpxi/9gDEAzsdF3lT8Mdso8xj4Kx7jp79QDrIBL40E4pSDaNeNMnU8+Yo1nrQVCO2JBEy3kpvn8pUnDjxZlBTZ9I4PkmH/Q"
}
});
}
});
// Step 1-g
window.__euid.callbacks.push((eventType: EventType, payload: CallbackPayload) => {
if (eventType !== 'SdkLoaded') {
if (payload.identity) {
const advertisingToken = payload.identity.advertising_token;
// Pass advertising_token to your advertising system to use
} else {
// No identity is available. Trigger a workflow for obtaining email address if you want to use EUID for targeted advertising.
}
}
});
The SDK invokes the specified callback function (which indicates the identity availability) and makes the established identity available client-side for bidding.
Depending on the structure of your code, it might be convenient to combine the callbacks for steps 1-f and 1-g into a single callback function.
Bid Using EUID Tokens
Based on the status and availability of a valid identity, the SDK does the following:
- Sets up the background token auto-refresh.
- Stores identity information in local storage or a first-party cookie.
- Uses the identity information to initiate requests for targeted advertising.
The bidding step is shown in the following table.
| Step | Endpoint/SDK | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 2-a | SDK for JavaScript | Gets the current user's advertising token by using the getAdvertisingToken() function as shown below. |
For an example of what an EUID token might look like in the bidstream, when it's sent from an SSP to a DSP, see What does an EUID token look like in the bidstream?.
<script>
let advertisingToken = __euid.getAdvertisingToken();
</script>
You need to consider how you pass the returned advertising token to SSPs. With some other approaches to client-side EUID implementation, such as using Prebid.js (see EUID Integration Overview for Prebid) or Google Ad Manager Secure Signals (see Google Ad Manager Secure Signals Integration Guide), the implementation includes functions that manage passing the returned advertising token. If you're using the SDK for JavaScript you'll need to manage this yourself.
Instead of calling __euid.getAdvertisingToken(), you can use the advertising_token property of the identity passed to the callback that you set up for step 1-g. The callback will be called every time the identity changes.
Refresh Tokens
As part of its initialization, the SDK sets up a token auto-refresh for the identity, which is triggered in the background by the timestamps on the identity or by failed refresh attempts due to intermittent errors.
| Step | Endpoint/SDK | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 3-a | SDK for JavaScript | The SDK automatically refreshes EUID tokens in the background. No manual action is required. |
| 3-b | SDK for JavaScript | If the user hasn't opted out, the POST /token/refresh endpoint automatically returns new identity tokens. |
Clear Identity: User Logout
The client lifecycle is complete when the user decides to log out from the publisher's site (not EUID). This closes the client's identity session and clears the first-party cookie information.
| Step | Endpoint/SDK | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 4-a | N/A | The user logs out from the publisher's asset. |
| 4-b | SDK for JavaScript | The SDK clears the EUID identity from the first-party cookie and disconnects the client lifecycle by using the disconnect() function as shown below. |
<script>
__euid.disconnect();
</script>
Sample Implementation
A sample implementation is available for client-server integration using the EUID SDK for JavaScript:
- Site: Client-Server EUID Integration Example using JavaScript SDK
- Code: uid2-examples/web-integrations/javascript-sdk/client-server
FAQs
For a list of frequently asked questions for the publisher audience, see FAQs for Publishers.